Dr. Kevin G. TeBeest
|
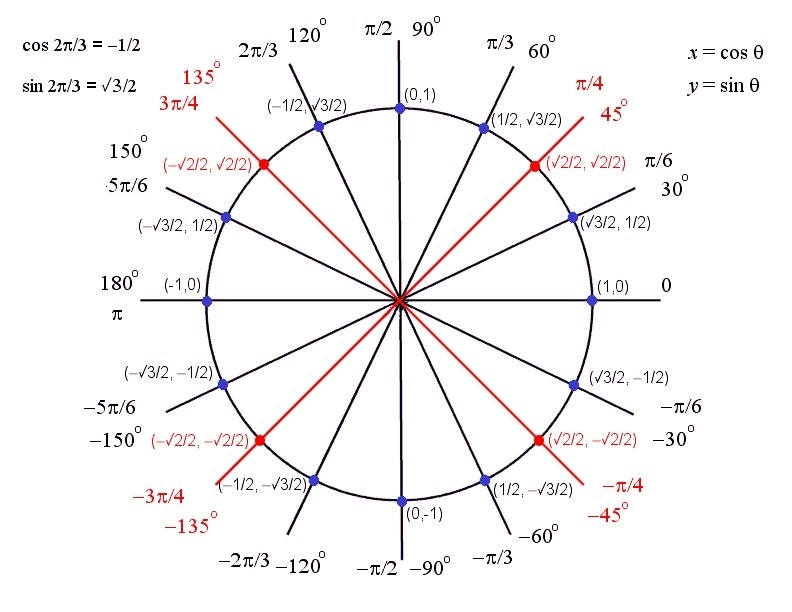
The unit circle (circle of radius 1) is a convenient way to memorize the cosine and sine values of the special angles. The special angles are angles that are integer multiples of π/6 radians (30º) and π/4 radians (45º). Recall that positive angles are measured counterclockwise from the +x axis. Using the cosine and sine of an angle, one may determine the angle's tangent, secant, cosecant, and cotangent. Because of the obvious symmetry, one need only memorize the cosine and sine of angles in Quadrant I; from that one may determine the trig values of angles in the other quadrants. Furthermore, one may determine the values all the trig functions (tangent, cotangent, secant, etc.) of the special angles shown. Some students prefer to memorize the table in Appendix D of our calculus text.
Dr. Kevin G. TeBeest, Copyright © 2003–2022
|