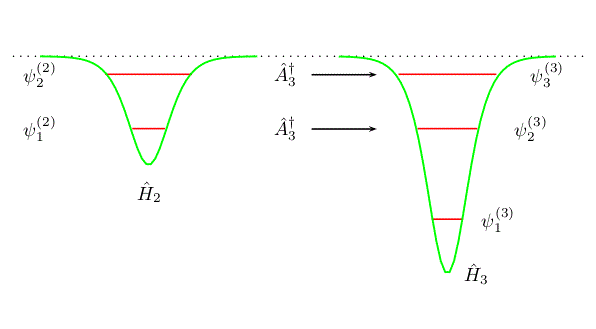
A Simplified Poschl-Teller Potential: An Instructive Exercise for Introductory Quantum Mechanics L. Hernández de la Peña , J. Chem. Educ. 95 ,1989 (2018)
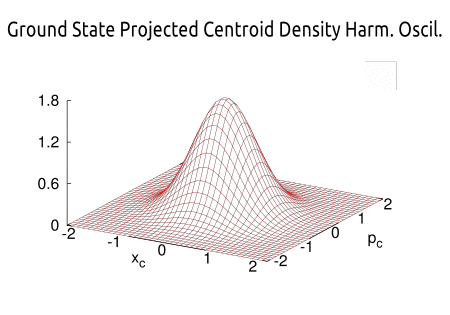
Formulation of State Projected Centroid Molecular Dynamics: Microcanonical Ensemble and Connection to the Wigner Distribution L. Hernández de la Peña and P.-N. Roy, J. Chem. Phys. 146 , 214116 (2017)
Sum Rule Constraints and The Quality of Approximate Kubo Transformed Correlation Functions L. Hernández de la Peña , J. Phys. Chem. B 120 , 965 (2016)
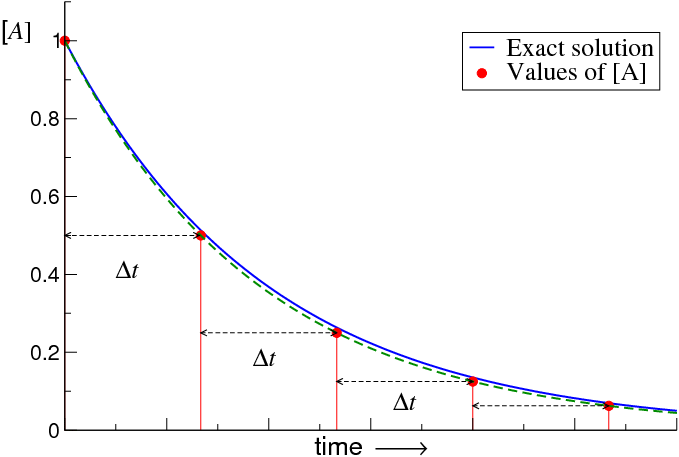
Solving Simple Kinetics Without Integrals L. Hernández de la Peña , J. Chem. Educ. 93 , 669 (2016)
On the zero temperature limit of the Kubo-transformed quantum time correlation function L. Hernández de la Peña , Mol. Phys. 112 , 929 (2014)
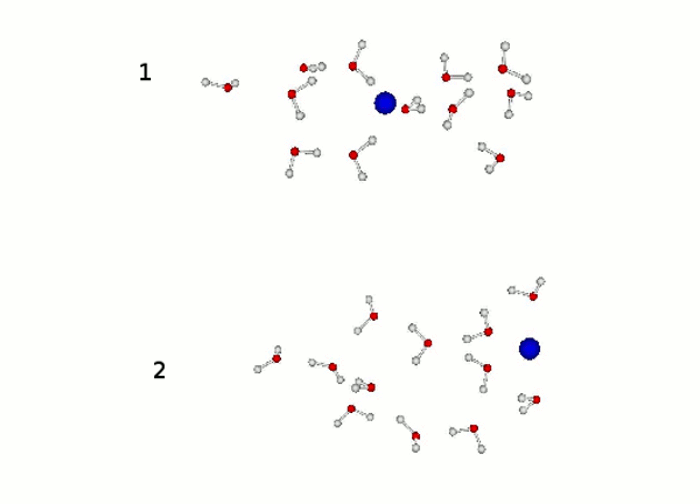
Quantum effects on the free energy of ionic water clusters evaluated by nonequilibrium computational methods L. Hernández de la Peña and G. H. Peslherbe, J. Phys. Chem. B 114 , 5404 (2010)
Quantum free energy differences from non-equilibrium path-integrals: II. Convergence properties for the harmonic oscillator L. Hernández de la Peña , G. H. Peslherbe and J. Schofield, Phys. Rev. E 78 , 041104 (2008) Annu. Rev. Condens. Matter Phys. 2 , 329 (2011);
Time: Poincare Seminar 2010 (Progress in Mathematical Physics) by B. Duplantier]
Quantum free energy differences from non-equilibrium path-integrals: I. Methods and numerical application L. Hernández de la Peña , G. H. Peslherbe and J. Schofield, Phys. Rev. E 78 , 041103 (2008) Annu. Rev. Condens. Matter Phys. 2 , 329 (2011);
Time: Poincare Seminar 2010 (Progress in Mathematical Physics) by B. Duplantier]
Discontinuous molecular dynamics for rigid bodies: Applications L. Hernández de la Peña , R. van Zon, J. Schofield and S. B. Opps, J. Chem. Phys. 126 , 074106 (2007)
Discontinuous molecular dynamics for semi-flexible and rigid bodies L. Hernández de la Peña , R. van Zon, J. Schofield and S. B. Opps, J. Chem. Phys. 126 , 074105 (2007) Nature Physics 9 , 554 (2013)]
Quantum effects in liquid water and ice: Model dependence L. Hernández de la Peña and P. G. Kusalik, J. Chem. Phys. 125 , 054512 (2006)
Quantum effects in ice Ih L. Hernández de la Peña , M. S. Gulam Razul and P. G. Kusalik, J. Chem. Phys. 123 , 144506 (2005)
Effects of quantization on the properties of liquid water L. Hernández de la Peña , M. S. Gulam Razul and P. G. Kusalik, J. Phys. Chem. A 109 , 7236-7241 (2005)
Temperature dependence of quantum effects in liquid water L. Hernández de la Peña and P. G. Kusalik, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127 , 5246-52 (2005)Molecular Modeling & Computational Chemistry Results: MMCC-Results 14 , 4 (2005)]
Quantum effects in light and heavy liquid water: A rigid body centroid molecular dynamics study L. Hernández de la Peña and P. G. Kusalik, J. Chem. Phys. 121 , 5992-6002 (2004)Science 315 , 1249 (2007)]
The rotational centroid and its application in quantum molecular dynamics simulations L. Hernández de la Peña and P. G. Kusalik, Mol. Phys. 102 , 927-938 (2004)